ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
Elasticity of demand explains the relationship between a change in price and consequent change in amount demanded.
Elastic demand: A small change in price may lead to a great change in quantity demanded. In this case, demand is elastic.
In-elastic demand: If a big change in price is followed by a small change in the quantity demanded, then the demand in “inelastic”.
Types of Elasticity of Demand:
1. Price elasticity of demand:
Marshall was the first economist to define price elasticity of demand. Price elasticity of demand measures changes in quantity demand to a change in Price. It is the ratio of percentage change in quantity demanded to a percentage change in price.
𝑷𝒓𝒊𝒄𝒆 𝒆𝒍𝒂𝒔𝒕𝒊𝒄𝒊𝒕𝒚 = 𝒑𝒓𝒐𝒑𝒐𝒓𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏𝒂𝒕𝒆 𝒄𝒉𝒂𝒏𝒈𝒆 𝒊𝒏 𝒕𝒉𝒆 𝒒𝒖𝒂𝒏𝒕𝒊𝒕𝒚 𝒅𝒆𝒎𝒂𝒏𝒅 𝒐𝒇 𝒄𝒐𝒎𝒎𝒐𝒅𝒊𝒕𝒚
𝒑𝒓𝒐𝒑𝒐𝒓𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏𝒂𝒕𝒆 𝒄𝒉𝒂𝒏𝒈𝒆 𝒊𝒏 𝒕𝒉𝒆 𝒑𝒓𝒊𝒄𝒆 𝒐𝒇 𝒄𝒐𝒎𝒎𝒐𝒅𝒊𝒕𝒚
There are five cases of price elasticity of demand





2. Income elasticity of demand:
Income elasticity of demand shows the change in quantity demanded as a result of a change in income. Income elasticity of demand may be slated in the form of a formula.
𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒 𝑒𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑡𝑦 = 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑝𝑜𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑑𝑒𝑚𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑜𝑓 𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑚𝑜𝑑𝑖𝑡𝑦
𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑝𝑜𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒
3. Cross elasticity of Demand:
A change in the price of one commodity leads to a change in the quantity demanded of another commodity. This is called a cross elasticity of demand. The formula for cross elasticity of demand is:
𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑒 𝑒𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑡𝑦 = 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑝𝑜𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑛𝑡𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑑𝑒𝑚𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑜𝑓 𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑚𝑜𝑑𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑥
𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑝𝑜𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 price of commodity y
a. In case of substitutes, cross elasticity of demand is positive. Eg: Coffee and Tea When the price of coffee increases, Quantity demanded of tea increases. Both are substitutes. Price of Coffee
b. Incase of compliments, cross elasticity is negative. If increase in the price of one commodity leads to a decrease in the quantity demanded of another and vice versa.
When price of car goes up from OP to OP!, the quantity demanded of petrol decreases from OQ to OQ!. The cross-demanded curve has negative slope.
4. Advertisement elasticity of Demand:
A change in the advertisement cost for a commodity leads to the change in the quantity demanded for a commodity.
𝐴𝑑𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑠𝑒𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑡𝑖𝑐𝑖𝑡𝑦 = 𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑝𝑜𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 quantity demanded 𝑜𝑓 𝑐𝑜𝑚𝑚𝑜𝑑𝑖𝑡𝑦
𝑝𝑟𝑜𝑝𝑜𝑟𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 advertisement of commodity
Measures of Elasticity of Demand:
A. Perfectly elastic demand:
When small change in price leads to an infinitely large change is quantity demand, it is called perfectly elastic demand. In this case (E=∞)
The demand curve is horizontal straight line. It shows the at “OP” price any amount is demand and if price increases, the consumer will not purchase the commodity.
B. Perfectly Inelastic Demand
In this case, even a large change in price fails to bring about a little or no change in quantity demanded.
When price increases from ‘OP’ to ‘OP’, the quantity demanded remains the same. In other words the response of demand to a change in Price is nil. In this case (‘E’=0)
C. Relatively elastic demand:
Demand changes more than proportionately to a change in price. i.e. a small change in price loads to a very big change in the quantity demanded. In this case (E > 1).
This demand curve will be flatter.
When price falls from ‘OP0’ to ‘OP1’, amount demanded in crease from “OQ0’ to “OQ1’ which is larger than the change in price
D. Relatively in-elastic demand.
Quantity demanded changes less than proportional to a change in price. A large change in price leads to small change in amount demanded. Here( E < 1)
Demanded carve will be steeper.
When price falls from “OP’ to ‘OP1 amount demanded increases from OQ to OQ1, which is smaller than the change in price.
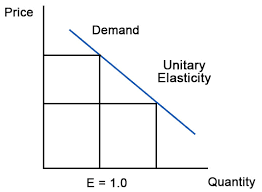
E. Unit elasticity of demand:
The change in demand is exactly equal to the change in price. When both are equal E=1 and elasticity if said to be unitary.
When price falls from ‘OP’ to ‘OP1’ quantity demanded increases from ‘OQ’ to ‘OQ1’. Thus a change in price has resulted in an equal change in quantity demanded so price elasticity of demand is equal to unity.
SIGNIFICANCE OF ELASTICITY OF DEMAND
The concept of elasticity is very useful to the producers and the policy makers. It is very valuable tool t decide the extent of increase or decrease in price for a desired change in the quantity demanded for the products and services in the firm or the economy.
The following are its applications-
a. To fix the prices of factors of production.
b. To fix the prices of goods and services provided rendered
c. To formulate or revise govt policies.
d. To forecast demand
e. To plan the level of output and price.
1. Prices of factors of production:
The factors o f production are land, labour, capital and organization and technology.we need to pay rent, wages, interest, profits and price for the factors of production.
2. Price fixation:
The manufacturer can decide the amount of prices that can be fixed for his product based on the concept of elasticity , if the manufacturer is monopoly, the manufacturer is free to fix as long as it does not attract the attention of the govt.If the demand for the product is inelastic, he can fix a higher price.
3. Govt policies
I. Tax policies: Govt extensively depends on this concept to finalise its policies relating to the taxes and revenue, where the product is such that the people cannot postpone its consumption, the govt tend to increase the prices. Eg: Petrol prices.
II. Raising bank deposits: If the govt wants to obilisr larger deposits from the customers , it proposes to raise the rates of fixed deposits marginally and vice versa.
III. Public Utilities: Govt uses the concept of elasticity in fixing charges for the public utilities such as electricity tariff, water charges.
IV. Revaluation or devaluation of currency: The govt has to study the impact of revaluation and devaluation on the interests of the exporter and importer.
4. Forecasting Demand:
The trade can estimate the quantity of goods to be sold at different income levels to raise the targeted revenue. The impact of changing income levels on the demand of the product can be assessed with the help of income elasticity.
5. Planning the level of output and price:
It helps the producer to evaluate whether a change in price will bring in adequate revenue or not, in general for items whose demand is elastic, it would benefit him to charge relatively low prices. If the demand for the product is inelastic, a little higher price may be helpful to him to get huge profits without losing sales